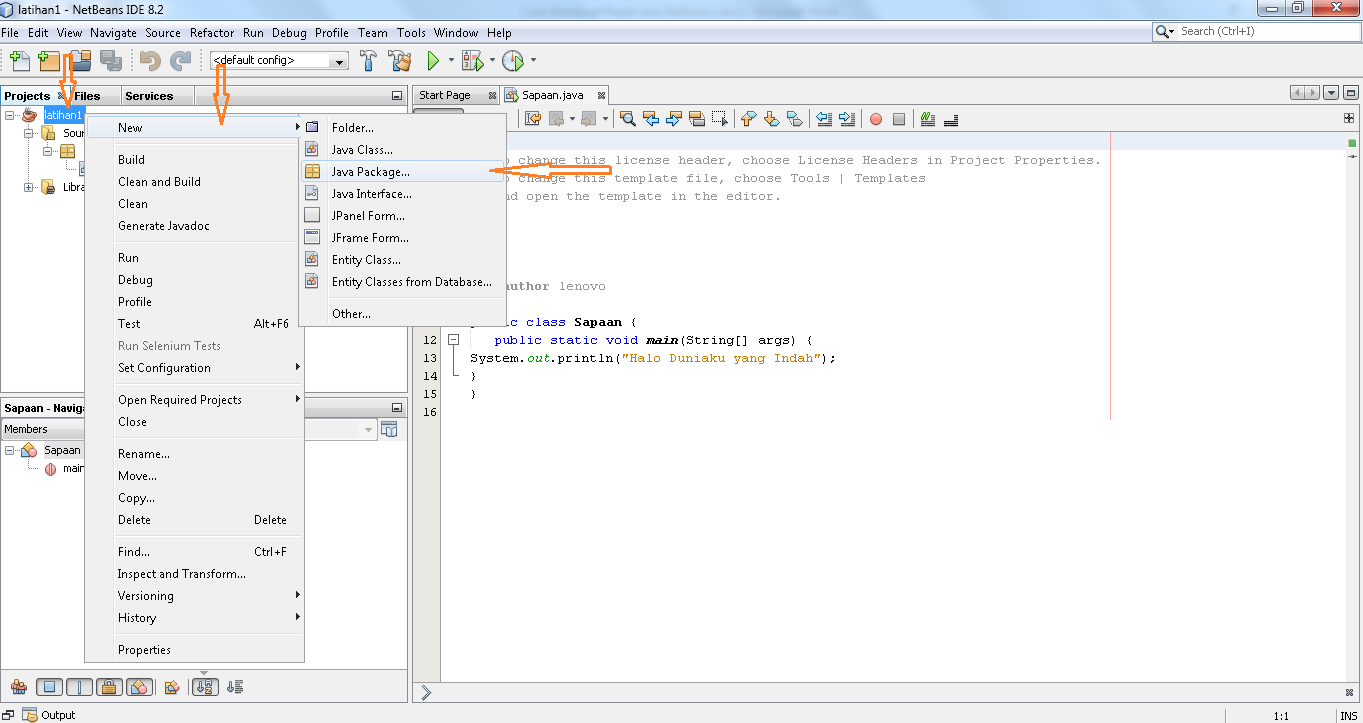
Cara Membuat Project Quality Plan
Membuat business plan akan membuat seorang pebisnis mengetahui arah setiap langkah bisnisnya. Berikut ini kami sajikan cara penyusunan business plan bagi Anda. Sebagai seorang pebisnis atau orang yang ingin memulai bisnis, Anda harus bisa membuat business plan atau minimal tahu apa itu business plan. This entry was posted in MS Project, Report, Dashboards and tagged cara buat s curve di ms project, Cara membuat S curve langsung di Microsoft project, cara membuat s-curve dengan ms project, cara membuat s-curve microsoft project, how to create s curve by ms project, import kurva s excel ke ms project, kurva s mudah, membuat kurva s, membuat.
For: Excel 2007 or later & Excel for iPad/iPhone Template Details License:(not for distribution or resale)Author: Jon WittwerDescriptionI like using Excel has a drawing canvas, especially for timelines, because the canvas is nearly infinite in size. A vertical timeline is easy to create using shape objects (lines, text boxes, callouts, etc.). You can use this template to give you a head start. Format a shape or callout the way you want and then use copy/paste to duplicate the shape and add your events.
Project TimelineA is typically used in business and engineering to plan and schedule projects. However, if you need a special project timeline to include in a presentation or some other document, you might want to try creating it using the drawing tools in Excel. This free spreadsheet below contains two example project schedules.(.xls)Time Period ComparisonsIn geneological (family history) research, timelines are particularly usefulfor comparing events and people's life spans.
This example spreadsheet uses stackedbar charts to compare a few different people living before and during the civilwar. By the way, if you're into family history, you may also want to try the new.(.xlsx)(.xls).
Cara Membuat Project Quality Planning
The Requirements Analysis Phase begins when the previous phase objectives have been achieved. Documentation related to user requirements from the Concept Development Phase and the Planning Phase shall be used as the basis for further user needs analysis and the development of detailed requirements. The following is a listing of deliverables required of all projects for this phase of work.DeliverableGoalsDeveloped ByApproved ByConcept of Operations – describes the characteristics of the proposed system from the users’ perspectives. Describe operational scenarios of system functions Identify modes of operationPlanning TeamAgency CIOProject SponsorBusiness OwnerProject ManagerSystem Requirements Document (SRD) – a formal statement of a system’s requirements, including, but not limited to: functional requirements, data requirements, system interface requirements, non-functional or operational requirements, and physical requirements.
Document detailed, measurable, consistent, and comprehensive system requirements Eliminate ambiguity of expectations regarding systemPlanning TeamAgency CIOProject SponsorBusiness OwnerProject ManagerRequirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) – a table that links requirements to their origins and traces them throughout the project life cycle. Developing the RTM helps to ensure that each requirement adds business value and that approved requirements are delivered. Establish a baseline for requirements change control, design, and testingPlanning TeamAgency CIOBusiness OwnerProject ManagerTest Master Plan (TMP) – documents the scope, content, methodology, sequence, management of, and responsibilities for test activities. Document and communicate tasks and activities needed to ensure that the system is adequately tested and can be successfully implementedProject ManagerAgency CIOBusiness OwnerAgency CIOBusiness OwnerProject ManagerAll deliverables other than those identified as Updates should be developed in this phase. Deliverables identified as Updates should be revisited and enhanced as necessary as prescribed in this phase.Deliverables produced during this phase must be reviewed in detail and should follow the approval path as defined in the above table. A signature page or section should accompany each deliverable requiring approval.DoIT will periodically request copies of these documents as part of its oversight responsibilities.3.0 RolesThe following personnel participate in the work activities in this phase:.
Agency CIO. Agency CFO. Project Sponsor. Executive Sponsor. Business Owner. Project Manager. Planning Team.
Project Stakeholders. Secretary of DoIT.
RACI KeyResponsible – Describes role that executes the activities to achieve the task.Accountable – Describes roles that own the quality of the deliverable and sign off on work that Responsible provides.Consulted – Describes roles that provide subject matter expertise.Informed – Describes roles who receive information about the task.The has detailed descriptions of these roles and their associated responsibilities.4.0 Tasks and Activities4.1 Review Phase Prerequisites.The Project Manager ensures the following prerequisites for this phase are complete:. To measure project effort at all life cycle phases, the Project Manager establishes timelines and metrics for success when planning project tasks. This project performance information must be used as an input to the monthly and quarterly reporting provided to the DoIT Project Management Office (PMO). The Project Manager also organizes and oversees systematic quality management reviews of project work as a part of project performance monitoring.The PMBOK provides additional details about controlling project work in sections 4.4 and 4.5, about project scope control in section 5.5, and about performance reporting in section 10.5.3.1. 4.3 Update PMP and Communication Management Plan.The Project Manager routinely updates the PMP (at least quarterly) to ensure the PMP reflects project performance accurately. Review project performance controls and risks for deviations from the baseline.Information dissemination is one of the Project Manager’s most important responsibilities. The Project Manager reviews and updates the Communication Management Plan at least quarterly to account for potential changes in project stakeholders.
The Project Manager distributes the updated PMP and risk management information according to the revised Communication Management Plan. PMBOK, Chapter 10 contains additional details regarding project communications and information distribution. 4.4 Perform Risk Management Activities.The Project Manager conducts risk management activities, including:. Identification – determination of risks, emerging risks, and risk characteristics. Risk Analysis – quantitative and/or qualitative analysis of each identified risk.
Usually, qualitative risk management techniques are the most applicable for State projects. Risk analysis methods, as well as the conditions under which each method might be used, are described in detail in PMBOK, Chapter 11. Response Planning – planning of methods for developing mitigation, transfer, or avoidance strategies to reduce risk. Monitoring and Control – definition of procedures to track risks, monitor residual risk, identify new risks, execute response plans, and evaluate risk management effectiveness. These activities occur throughout project duration to track and mitigate any new or changed project risks. The results of risk monitoring and control activities must be documented in the project’s Risk Register and included in monthly and quarterly reporting to DoIT PMO.
The PMBOK has details for risk management activities in section 11, particularly sections 11.2 through 11.6. PMBOK, fourth edition, section 5.1.2, has additional information regarding tools and techniques for requirements analysis. During requirements elicitation, the Planning Team should note all assumptions and constraints that will affect development and operation of the system. Requirements should also be prioritized based on relative importance and by when they are needed.In addition to functional requirements, requirements analysis identifies non-functional requirements such as operational and technical requirements. Non-functional requirements describe characteristics or specific parameters of the system and include audit, availability, interface, capacity, performance, usage, security, back-up, physical, and site requirements.The Planning Team should describe the system as the functions to be performed and not specific hardware, programs, files and data streams. The requirements must be unambiguous (measurable and testable), traceable, complete, consistent, and approved.The Planning Team may perform these activities concurrently and iteratively to refine the set of requirements. The requirements’ level of detail should be sufficient to develop information for deliverables as well as remaining procurement documents.
All requirements must be consistent with the on the DoIT web site. 4.6 Develop the Concept of Operations. 4.6.1 Document DescriptionThe Concept of Operations document describes the characteristics of the proposed system from the users’ perspectives.
Additional information may be found in the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IEEE) Guide for Information Technology – System Definition – Concept of Operations (ConOps) Document. Agencies may use the to help ensure that all appropriate testing activities are defined and documented. 4.12.3 Guidance for Document DevelopmentThe Project Manager should specify in the TMP how test activities will be managed, including organization, relationships, and responsibilities.
The TMP should also document how test results will be verified and how the system will be validated.The Project Manager updates the RTM to include a TMP reference that indicates the testing of each requirement. Elaboration of testing plans occurs in the Design and Development Phases. 4.12.4 Dos and Don'ts.
Do consider all types of testing activities required to meet project requirements. Do involve end users in determining the nature and extent of tests to be conducted. Do address how the TMP will be updated to include progressively more detail as the system is developed.4.13 Perform Phase-Closure Activities.The Project Manager and the Planning Team prepare and present a project status review for the Agency CIO, Project Sponsor, Executive Sponsor, and other project stakeholders after completing all Requirements Analysis Phase tasks. This review addresses:. Status of Requirements Analysis Phase activities. Planning status for all subsequent life cycle phases, with significant detail about the Design Phase (such as the status of pending contracts). Status on resource availability.
Project scope control as described in the PSS. Changes to the project schedule and estimated completion date. 'Go-No Go' decision made to proceed to next phase, based on Requirements Analysis Phase information. Verification that all changes are conducted in accordance with the approved Change Management Plan. The Project Manager compares actual project performance to the PMP and the projected cost of the project to determine any variances from the cost baseline during the phase-end review.
Cara Membuat Project Quality Plan Template
The Project Manager also performs a comprehensive risk assessment of the project to update the Risk Register before beginning the next phase, Design.The Project Manager must obtain deliverable approval signatures before proceeding to the Design Phase.Update the project documentation repository upon completion of the phase-closure activities.5.0 ConclusionsThe approval of the System Requirements Document, RTM, and the TMP as well as the completion of the Requirements Analysis project status review and approval to proceed to the next phase signify the end of the Requirements Analysis Phase..